参考——温湿度传感器DHT11驱动_STM32
设备:stm32f407ZGT6
环境:FreeRTOS HAL
一、简介
到网上找DHT11的驱动,但是都无法使用。原因是RTOS环境中,由于多线程,使用循环计数阻塞式的delay_us延时函数就没那么准,且不同设备中delay_us的计数值不一样。而DHT11对时序要求得又十分严格,这就会导致读取数据异常,甚至无法读取。
/**********************************************************************************************************
函数名称:us延时函数,最小延时为1us
输入参数:时间
输出参数:无
**********************************************************************************************************/
void delay_us(unsigned int time)
{
unsigned short i = 0;
while (time--)
{
i = 8;
while (i--)
;
}
}而且这个DHT11间隔若干秒连续读取一段时间后,会在某次读取第一个完整字节后就会莫名其妙卡住,不知道是不是硬件的问题。这个没有什么好办法解决,在读取的时候加个超时判断语句,超时就返回false
虽然考虑过使用其他方法达到更精准的微秒级延时,但还是想尝试一下用不那么精准的方法来完成。于是下面就简单的使用计数值来模拟延时,不需要考虑延时多少微秒,只需要比较高电平持续时间的相对长短。
二、代码
1,简略分析
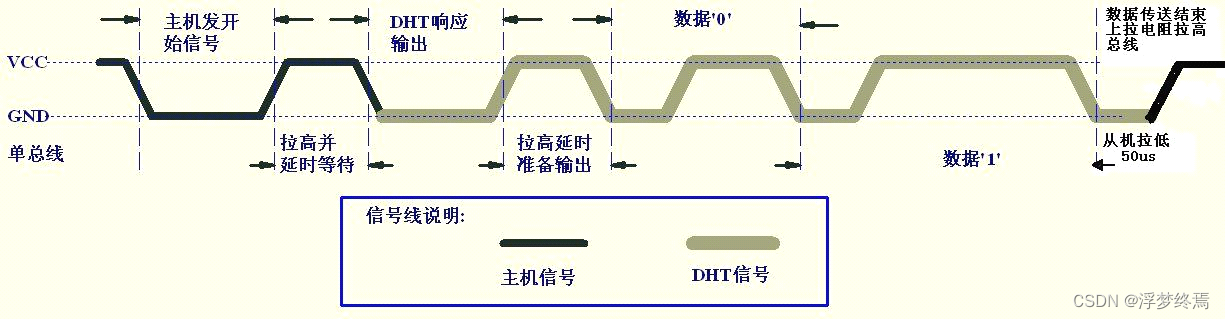
时序很好分析。分为主机部分和DHT部分。通信的整个过程是主机先向DHT发送开始信号,如果DHT回应了(大多数情况都会回应,除非延时不准),那么就读取数据,读取结束后再拉高(实测过程中,这个加不加都会间歇性卡住。这里没有加)
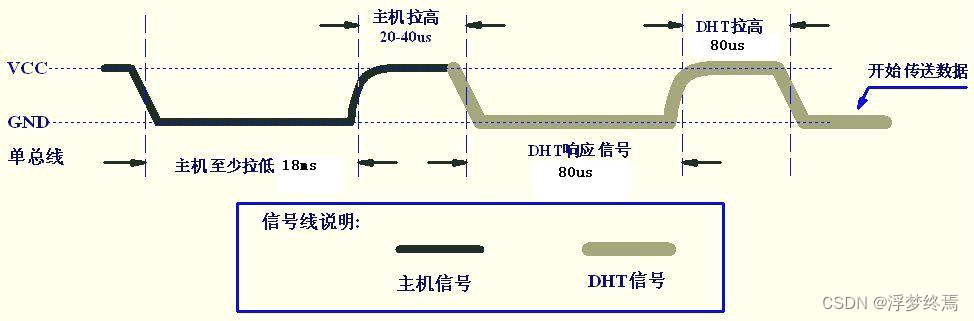
发送开始信号
inline void DHT11_Rst()
{
DHT11_OUT();
DHT11_Low();
osDelay(30);//根据时序图可知,需要至少拉低18ms。换成自己的延时函数,不需要太准
DHT11_High();
std_delay_25us();//20-40us,不需要太准,它与它上面的那行代码也可以不加
}
检测DHT响应
inline void DHT11_Check()
{
DHT11_IN();
while (DHT11_Read())
;
while (!DHT11_Read())
;
}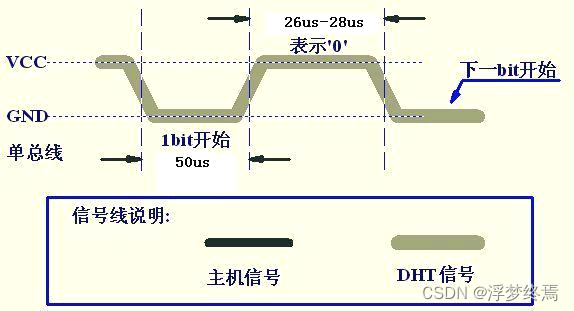
读取一位数据
当DHT输出响应后会拉高一段时间,然后才会拉低,进入一个50us的低电平间隙,等再次拉高时就是读取数据的时候
此后在读取上一位数据结束后,都会拉低50us,然后再次拉高来读取数据
根据上面两种情况,所以统一先等待拉低,以便进入50us的低电平间隙。然后再等待拉高,以便读取数据,最后再等待拉低,在这两个操作中用计数值来记录时间长短。
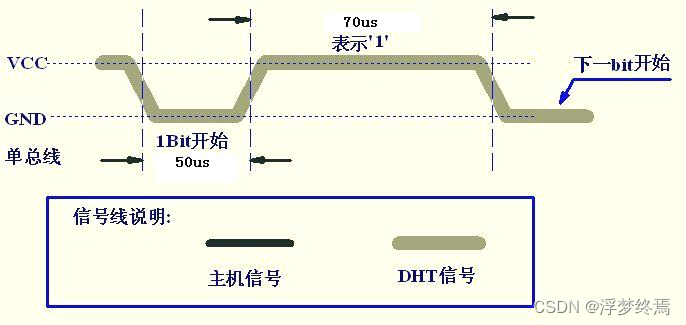
0:26-28us
1:70us
while (DHT11_Read()) {} // 等待低电平
while (!DHT11_Read()) {}// 等待变高电平
// 开始读数据
uint16_t time_count = 0;
for (; DHT11_Read() && time_count = DHT11_MAX_DELAY_COUNT)
{
return false;
}
timeBuf[timeBufIndex++] = time_count >> 4;// 存储计数值,由于事先已经知道一个为上面这个读取一位数据是可以简化的,因为按照下面读取的规则,其实是不需要每次都要在开头等待低电平。但是检测DHT输出响应后需要等待低电平
简化后是这样的,读取一位数据不需要考虑很多,只需要等待变为高电平就行了。但是检测DHT11响应考虑的就比较多了,需要再次等待低电平。
inline void DHT11_Check()
{
DHT11_IN();
while (DHT11_Read()) //等待低电平
;
while (!DHT11_Read()) //等待高电平
;//也可以在这里计数,用于测量80us所需的计数值,从而测算出20us、40us等对应的计数值
while (DHT11_Read()) {} // 等待低电平
}
while (!DHT11_Read()) {}// 等待变高电平
// 开始读数据
uint16_t time_count = 0;
for (; DHT11_Read() && time_count = DHT11_MAX_DELAY_COUNT)
{
return false;
}
timeBuf[timeBufIndex++] = time_count >> 4;// 存储计数值,由于事先已经知道一个为读取一个字节
这个只要一个for循环即可,循环8次。这里是未简化的版本。读取5个字节就是再套个for循环,循环5次即可
//读取一字节
for (uint8_t j = 0; j < 8; j++)
{
while (DHT11_Read()) {} // 等待低电平
while (!DHT11_Read()) {}// 等待变高电平
// 开始读数据
uint16_t time_count = 0;
for (; DHT11_Read() && time_count = DHT11_MAX_DELAY_COUNT)
{
return false;
}
timeBuf[timeBufIndex++] = time_count >> 4;// 存储计数值,由于事先已经知道一个为875,一个为275左右,所以除以16
}数据处理
使用中位数来区分高电平持续的时间是长是短,以便判断是1还是0。正常情况下,这个持续时间差别很明显。
//找出最大计数值和最小计数值,用以判断是1还是0
uint16_t timeMax = 0;
uint16_t timeMin = 0xFFFF;
for (unsigned short i: timeBuf)
{
if (i > timeMax) timeMax = i;
if (i > 1;// 取中位数,以区分时间长短
// 转为二进制数据,进而转为字节数据
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
uint8_t data = 0;
for (uint8_t j = 0; j < 8; j++)
{
data < timeMed);
}
buf[i] = data;// 存储数据
}2,完整代码
需要注意的是,下面代码使用的是C++,如果你使用的是C,那么用相应功能的代码替换掉即可。bool类型需要包含stdbool头文件
DHT11.h
头文件里未被注释的接口,决定了哪些函数需要重点关注
#ifndef DHT11_H
#define DHT11_H
void DHT11_Init();
//bool DHT11_Read_Data(float &temp,float &humi);
bool DHT11_Read_Data_Fast_Pro(float &temp, float &humi);//自定义的快速读取函数
#endif//DHT11_H
DHT11.cpp
里面的这个std_delay_us是用于调试中用的,在void DHT11_Rst()函数里,你把延时换成你自带的即可,这个不需要多精准。
下面的函数是与时序图直接对应的,连续读取温度时,最好间隔1s以上。
后面还有一个版本
#include "DHT11.h"
#include "cmsis_os2.h"
#include "stm32f4xx_hal.h"
#define DHT11_Pin GPIO_PIN_6
#define DHT11_Pin_Location 6 //第几个引脚就写几
#define DHT11_GPIO_Port GPIOE
#define DHT11_GPIO_CLK_ENABLE() __HAL_RCC_GPIOE_CLK_ENABLE()
#define DHT11_MAX_DELAY_COUNT 7000//防止卡死
#define DHT11_Read() (DHT11_GPIO_Port->IDR & DHT11_Pin) /*HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(DHT11_GPIO_Port, DHT11_Pin)*/
#define DHT11_High() DHT11_GPIO_Port->ODR |= (0x01 <ODR &= ~(0x01 <MODER &= ~(3 <MODER |= 0 <MODER &= ~(3 <MODER |= 1 << 2 * DHT11_Pin_Location; \
}
//static uint16_t std_delay_80us = 875;//事先测试过
//static uint16_t std_delay_50us = 566;
/**动态计算延时,以确保任何情况下都可以得到较为准确的延时*/
//根据80us的那段时序,通过计数值得到80us需要的计数值,然后以此测算不同us的延时,在Check函数里,这里省略了
//void std_delay_us(uint8_t us)
//{
// // uint16_t count = std_delay_80us * us / 80;//测试得到的,但乘法会有很大的延时,所以只能作为计算公式
// uint16_t count = 11 * us;
// for (uint16_t i = 0; i < count; ++i)
// ;
//}
//这个延时函数可以换成自己的延时,因为设备不同、代码环境不同,延时的计数就不同
//可以通过上面那个方法来计算,测算的是Check函数里的80s延时
inline void std_delay_25us()
{
for (uint16_t i = 0; i < 20; ++i)//单个任务时为273
;
}
/**函数*/
inline void DHT11_Rst();
void DHT11_Init()
{
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct = {0};
DHT11_GPIO_CLK_ENABLE();
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = DHT11_Pin;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT_PP;
GPIO_InitStruct.Pull = GPIO_PULLUP;
// GPIO_InitStruct.Speed = GPIO_SPEED_FREQ_VERY_HIGH;
HAL_GPIO_Init(DHT11_GPIO_Port, &GPIO_InitStruct);
DHT11_High();
}
inline void DHT11_Rst()
{
DHT11_OUT();
DHT11_Low();
osDelay(30);//根据时序图可知,需要至少拉低18ms
DHT11_High();
std_delay_25us();//20-40us
}
inline void DHT11_Check()
{
DHT11_IN();
while (DHT11_Read())
;
while (!DHT11_Read())
;
}
// 全局变量
static uint8_t timeBuf[40];// 存储计数值
static uint8_t timeBufIndex = 0;
bool DHT11_Read_Data_Fast_Pro(float &temp, float &humi)
{
static uint8_t buf[5];
DHT11_Rst(); // 设置输出模式
DHT11_Check();// 设置输入模式
timeBufIndex = 0; // 重置计数值索引
for (unsigned char &i: buf)// 读取40位数据
{
// DHT11_Read_Byte_Fast_Pro();
//读取一字节
for (uint8_t j = 0; j < 8; j++)
{
while (DHT11_Read()) {} // 等待低电平
while (!DHT11_Read()) {}// 等待变高电平
// 开始读数据
uint16_t time_count = 0;
for (; DHT11_Read() && time_count = DHT11_MAX_DELAY_COUNT)
{
return false;
}
timeBuf[timeBufIndex++] = time_count >> 4;// 存储计数值,由于事先已经知道一个为875,一个为275左右,所以除以16
}
}
//找出最大计数值和最小计数值,用以判断是1还是0
uint16_t timeMax = 0;
uint16_t timeMin = 0xFFFF;
for (unsigned short i: timeBuf)
{
if (i > timeMax) timeMax = i;
if (i > 1;// 取中位数
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
uint8_t data = 0;
for (uint8_t j = 0; j < 8; j++)
{
data < timeMed);
}
buf[i] = data;// 存储数据
}
//校验数据
if ((buf[0] + buf[1] + buf[2] + buf[3]) == buf[4])
{
humi = (buf[0] * 10 + buf[1]) / 10.0f;
temp = (buf[2] * 10 + buf[3]) / 10.0f;
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}里面有多个版本,第0个是特化版本,其下愈为通用。只有第1个版本(没有注释的)加了防卡死的判断语句
#include "DHT11.h"
#include "cmsis_os2.h"
#include "stm32f4xx_hal.h"
#define DHT11_Pin GPIO_PIN_6
#define DHT11_Pin_Location 6
#define DHT11_GPIO_Port GPIOE
#define DHT11_GPIO_CLK_ENABLE() __HAL_RCC_GPIOE_CLK_ENABLE()
#define DHT11_MAX_DELAY_COUNT 4000//防止卡死
#define USE_YZHX 1 //优化等级,分为0,1,2,3
#define DHT11_Read() (DHT11_GPIO_Port->IDR & DHT11_Pin) /*HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(DHT11_GPIO_Port, DHT11_Pin)*/
#define DHT11_High() DHT11_GPIO_Port->ODR |= (0x01 <ODR &= ~(0x01 <MODER &= ~(3 <MODER |= 0 <MODER &= ~(3 <MODER |= 1 << 2 * DHT11_Pin_Location; \
}
//static uint16_t std_delay_80us = 875;//事先测试过
//static uint16_t std_delay_50us = 566;
/**动态计算延时,以确保任何情况下都可以得到较为准确的延时*/
//void std_delay_us(uint8_t us)
//{
// // uint16_t count = std_delay_80us * us / 80;//测试得到的
// uint16_t count = 11 * us;
// for (uint16_t i = 0; i < count; ++i)
// ;
//}
inline void std_delay_25us()
{
for (uint16_t i = 0; i < 20; ++i)//单个任务时,大概为273
;
}
void DHT11_Init()
{
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct = {0};
DHT11_GPIO_CLK_ENABLE();
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = DHT11_Pin;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT_PP;
GPIO_InitStruct.Pull = GPIO_PULLUP;
// GPIO_InitStruct.Speed = GPIO_SPEED_FREQ_VERY_HIGH;//输入模式下,最好不要配置速度,所以为了兼容输入就不配置了,即默认2MHz
HAL_GPIO_Init(DHT11_GPIO_Port, &GPIO_InitStruct);
DHT11_High();
}
inline void DHT11_Rst()
{
DHT11_OUT();
DHT11_Low();
osDelay(25);//根据时序图可知,需要至少拉低18ms
DHT11_High();
std_delay_25us();//20-40us
}
inline void DHT11_Check()
{
DHT11_IN();
//等待低电平
DHT11_Wait_Low();
//等待高电平
DHT11_Wait_High();
// 等待低电平
DHT11_Wait_Low();
}
#if USE_YZHX == 0
bool DHT11_Read_Data_Fast_Pro(float &temp, float &humi)
{
static uint8_t buf[5];
DHT11_Rst(); // 设置输出模式
DHT11_Check();// 设置输入模式
for (unsigned char &i: buf)// 读取40位数据
{
uint8_t data = 0;
for (uint8_t j = 0; j < 8; j++)
{
data <> 10;// 由于事先已经知道一个为1194,一个为406左右
}
i = data;// 存储数据
}
if ((buf[0] + buf[1] + buf[2] + buf[3]) == buf[4])
{
humi = (buf[0] * 10 + buf[1]) / 10.0f;
temp = (buf[2] * 10 + buf[3]) / 10.0f;
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
#endif
/********************下面为次优级优化********************/
#if USE_YZHX == 1
// 全局变量
static uint8_t timeBuf[40];// 存储计数值
static uint8_t timeBufIndex = 0;
//void DHT11_Read_Byte_Fast_Pro()
//{
// for (uint8_t i = 0; i >4;// 存储计数值,由于事先已经知道一个为875,一个为275左右,所以除以16
// }
//}
bool DHT11_Read_Data_Fast_Pro(float &temp, float &humi)
{
static uint8_t buf[5];
DHT11_Rst(); // 设置输出模式
DHT11_Check();// 设置输入模式
timeBufIndex = 0; // 重置计数值索引
for (unsigned char &i: buf)// 读取40位数据
{
// DHT11_Read_Byte_Fast_Pro();
//读取一字节
for (uint8_t j = 0; j < 8; j++)
{
DHT11_Wait_High();// 等待变高电平
// 开始读数据
uint16_t time_count = 0;
for (; DHT11_Read() && time_count = DHT11_MAX_DELAY_COUNT)
{
return false;
}
timeBuf[timeBufIndex++] = time_count >> 4;// 存储计数值,由于事先已经知道一个为875,一个为275左右,所以除以16
}
}
// std_delay_25us();
// std_delay_25us();
// DHT11_OUT();
// DHT11_High();
uint16_t timeMax = 0;
uint16_t timeMin = 0xFFFF;
for (unsigned short i: timeBuf)
{
if (i > timeMax) timeMax = i;
if (i > 1;// 取中位数
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
uint8_t data = 0;
for (uint8_t j = 0; j < 8; j++)
{
data < timeMed);
}
buf[i] = data;// 存储数据
}
if ((buf[0] + buf[1] + buf[2] + buf[3]) == buf[4])
{
humi = (buf[0] * 10 + buf[1]) / 10.0f;
temp = (buf[2] * 10 + buf[3]) / 10.0f;
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
#endif
#if USE_YZHX == 2
static uint16_t timeBuf[40];//存储计数值
static uint8_t timeBufIndex = 0;
void DHT11_Read_Byte_Fast_Pro()
{
for (uint8_t i = 0; i timeMax)
{
timeMax = i;
}
else if (i > 1;//整除2,取中位数
bool tempBin;
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
data = 0;
for (uint8_t j = 0; j < 8; j++)
{
data < timeMed)
{
tempBin = true;
}
else
{
tempBin = false;
}
data |= tempBin;
}
buf[i] = data;//存储数据
}
/**检验**/
if ((buf[0] + buf[1] + buf[2] + buf[3]) == buf[4])
{
humi = (float) (buf[0] + buf[1] * 0.1);
temp = (float) (buf[2] + buf[3] * 0.1);
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
#endif
/********************下面为原版优化********************/
#if USE_YZHX == 3
static uint16_t timeBuf[40];//存储计数值
void DHT11_Read_Byte_Fast_Pro()
{
static uint8_t timeBufIndex = 0;//存储计数值索引
for (uint8_t i = 0; i timeMax)
{
timeMax = i;
}
else
{
timeMin = i;
}
}
std_delay_25us();
std_delay_25us();
DHT11_OUT();
DHT11_High();
/**把计数值转为二进制数据*/
uint16_t timeMed = (timeMax + timeMin) >> 1;//整除2,取中位数
uint8_t data; //临时数据
bool tempBin; //临时二进制数据
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
data = 0;//重置
for (int j = 0; j < 8; ++j)
{
data < timeMed)
{
tempBin = true;
}
else
{
tempBin = false;
}
data |= tempBin;
}
buf[i] = data;//存储数据
}
/**检验**/
if ((buf[0] + buf[1] + buf[2] + buf[3]) == buf[4])
{
humi = (float) (buf[0] + buf[1] * 0.1);
temp = (float) (buf[2] + buf[3] * 0.1);
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
#endif



