Linux网络 – json,网络计算服务器与客户端改进
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、json
- 1.引入库
- 2. 使用步骤
- 2.Calculator.hpp
- 3.Task.hpp
- 4.serverCal.hpp
- 新客户端
前言
本章内容主要对上一章的网络计算器客户端和服务器进行一些Bug修正与功能改进。 并学习如何使用json库和daemon函数。
一、json
在我们自己的电脑上一些软件的文件夹中,我们经常能看到.json后缀的文件,那么这种文件是用来干什么的呢?
这就要说到我们上节课所讲的序列化和反序列化了,相信如果大家自己如果尝试写了一遍之后,会发现序列化和反序列化还是比较难写的。
而市面上,是存在这么一个库被广泛引用来做序列化和反序列化,他就是json库。
json库是一个第三方库,所以我们的Linux服务器一般是不自带的,需要下载安装。
sudo yum install -y jsoncpp-devel
安装后,它的头文件位于
ls /usr/include/jsoncpp/json
因为是第三方库,所以它也需要链接动态库。
ls /lib64/libjsoncpp.so

1.引入库
代码如下(示例):
#include
g++编译
Lib=-ljsoncpp
serverCal:main.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++11 -lpthread $(Lib)
clientCal:clientCal.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++11 $(Lib)
2. 使用步骤
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include "log.hpp"
#include
extern Log lg;
const char blank_space_sep = ' ';
const char protocol_sep = '
';
enum Code
{
Div_Zero_Err = 1,
Mod_Zeor_Err,
Operatorr_Err,
Float_Mod_Err
};
enum Type
{
Type_Int = 1,
Type_Double = 2
};
// 多态版本
bool CheckType(std::string &in_str, int* type)
{
Json::Value root;
Json::Reader reader;
bool suc = reader.parse(in_str, root);
if (!suc)
{
lg(Warning, "Deserialize Failed...");
return false;
}
*type = root["type"].asInt();
return true;
}
class Request
{
public:
Request() {}
Request(char op)
: _op(op) {}
virtual bool serialize() {}
virtual bool deserialize() {}
public:
char _op;
};
class IntRequest : public Request
{
public:
IntRequest() {}
IntRequest(int x, int y, char op)
: _x(x), _y(y), Request(op) {}
virtual bool serialize(std::string *out_str)
{
Json::Value root;
root["x"] = _x;
root["y"] = _y;
root["op"] = _op;
root["type"] = 1;
Json::FastWriter writer;
*out_str = writer.write(root);
return true;
}
virtual bool deserialize(std::string &in_str)
{
Json::Value root;
Json::Reader reader;
bool suc = reader.parse(in_str, root);
if (!suc)
{
lg(Warning, "Request Deserialize Failed...");
return false;
}
_x = root["x"].asInt();
_y = root["y"].asInt();
_op = root["op"].asInt();
Json::FastWriter writer;
in_str.erase(0, writer.write(root).size());
std::cout << "已经删除已解析报头..." << std::endl;
return true;
}
public:
int _x;
int _y;
};
class DoubleRequest : public Request
{
public:
DoubleRequest() {}
DoubleRequest(double x, double y, char op)
: _x(x), _y(y), Request(op) {}
virtual bool serialize(std::string *out_str)
{
Json::Value root;
root["x"] = _x;
root["y"] = _y;
root["op"] = _op;
root["type"] = 2;
Json::FastWriter writer;
*out_str = writer.write(root);
return true;
}
virtual bool deserialize(std::string &in_str)
{
Json::Value root;
Json::Reader reader;
bool suc = reader.parse(in_str, root);
if (!suc)
{
lg(Warning, "Request Deserialize Failed...");
return false;
}
_x = root["x"].asDouble();
_y = root["y"].asDouble();
_op = root["op"].asInt();
Json::FastWriter writer;
in_str.erase(0, writer.write(root).size());
return true;
}
public:
double _x;
double _y;
};
class Respond
{
public:
Respond() {}
Respond(int code)
: _code(code) {}
virtual bool serialize() {}
virtual bool deserialize() {}
public:
int _code = -1;
};
class IntRespond : public Respond
{
public:
IntRespond() {}
IntRespond(int result, int code)
: _result(result), Respond(code) {}
virtual bool serialize(std::string *out_str)
{
Json::Value root;
root["result"] = _result;
root["code"] = _code;
root["type"] = 1;
Json::FastWriter writer;
*out_str = writer.write(root);
return true;
}
virtual bool deserialize(const std::string &in_str)
{
Json::Value root;
Json::Reader reader;
bool suc = reader.parse(in_str, root);
if (!suc)
{
lg(Warning, "Respond Deserialize Failed...");
return false;
}
_result = root["result"].asInt();
_code = root["code"].asInt();
return true;
}
public:
int _result;
};
class DoubleRespond : public Respond
{
public:
DoubleRespond() {}
DoubleRespond(double result, int code)
: _result(result), Respond(code) {}
virtual bool serialize(std::string *out_str)
{
Json::Value root;
root["result"] = _result;
root["code"] = _code;
root["type"] = 2;
Json::FastWriter writer;
*out_str = writer.write(root);
return true;
}
virtual bool deserialize(const std::string &in_str)
{
Json::Value root;
Json::Reader reader;
bool suc = reader.parse(in_str, root);
if (!suc)
{
lg(Warning, "Respond Deserialize Failed...");
return false;
}
_result = root["result"].asDouble();
_code = root["code"].asInt();
return true;
}
public:
double _result;
};
2.Calculator.hpp
#pragma once
#include "protocol.hpp"
class Calculator
{
public:
Calculator() {}
IntRespond calculate(const IntRequest &rq)
{
IntRespond rs;
switch (rq._op)
{
case '+':
rs._result = rq._x + rq._y;
break;
case '-':
rs._result = rq._x - rq._y;
break;
case '*':
rs._result = rq._x * rq._y;
break;
case '/':
if (rq._y == 0)
{
lg(Warning, "Found Div Zero Error...");
rs._code = Div_Zero_Err;
return rs;
}
rs._result = rq._x / rq._y;
break;
case '%':
if (rq._y == 0)
{
lg(Warning, "Found Mod Zero Error...");
rs._code = Mod_Zeor_Err;
return rs;
}
rs._result = rq._x % rq._y;
break;
default:
lg(Warning, "Found Operator Error...");
rs._code = Operatorr_Err;
return rs;
}
rs._code = 0;
return rs;
}
DoubleRespond calculate(const DoubleRequest &rq)
{
DoubleRespond rs;
switch (rq._op)
{
case '+':
rs._result = rq._x + rq._y;
break;
case '-':
rs._result = rq._x - rq._y;
break;
case '*':
rs._result = rq._x * rq._y;
break;
case '/':
if (rq._y == 0)
{
lg(Warning, "Found Div Zero Error...");
rs._code = Div_Zero_Err;
return rs;
}
rs._result = rq._x / rq._y;
break;
case '%':
lg(Warning, "Float Mod Error...");
rs._code = Float_Mod_Err;
return rs;
default:
lg(Warning, "Found Operator Error...");
rs._code = Operatorr_Err;
return rs;
}
rs._code = 0;
return rs;
}
};
3.Task.hpp
#pragma once
#include "Socket.hpp"
#include "protocol.hpp"
#include "Calculator.hpp"
class Task
{
public:
Task(int socket_fd)
: _socket_fd(socket_fd)
{
}
void IntHandle(std::string &message)
{
IntRequest rq;
Calculator cal;
// 因为可能message里面已经存在了多个报文,所以就需要一次性多次处理
if (!rq.deserialize(message))
{
// 反序列化失败说明里面的数据可能出现数据丢失等情况,出现这种情况说明我们的报文数据不再可信,最直接的办法就是丢弃全部报文!
message = "";
return;
}
IntRespond rs = cal.calculate(rq);
std::string res;
rs.serialize(&res);
printf("%d %c %d = %d
", rq._x, rq._op, rq._y, rs._result);
write(_socket_fd, res.c_str(), res.size());
}
void DoubleHandle(std::string &message)
{
DoubleRequest rq;
Calculator cal;
// 因为可能message里面已经存在了多个报文,所以就需要一次性多次处理
if (!rq.deserialize(message))
{
// 反序列化失败说明里面的数据可能出现数据丢失等情况,出现这种情况说明我们的报文数据不再可信,最直接的办法就是丢弃全部报文!
message = "";
return;
}
DoubleRespond rs = cal.calculate(rq);
std::string res;
rs.serialize(&res);
printf("%lf %c %lf = %lf
", rq._x, rq._op, rq._y, rs._result);
write(_socket_fd, res.c_str(), res.size());
}
void run()
{
char in_buffer[1024];
std::string message = "";
while (true)
{
memset(in_buffer, 0, sizeof in_buffer);
int n = read(_socket_fd, (void *)in_buffer, sizeof in_buffer - 1);
if (n == 0)
{
lg(Warning, "Connection closed by foreign host, socketfd[%d] closed...", _socket_fd);
break;
}
else if (n < 0)
{
lg(Warning, "Read Error, socketfd[%d]...", _socket_fd);
break;
}
in_buffer[n] = 0;
message = in_buffer;
std::cout << "报文大小: " << message.size() << " ,报文内容: " << message << std::endl;
// 判断发来的数据类型
while (!message.empty())
{
int type;
if (!CheckType(message, &type))
{
//报文内容出现问题
message = "";
break;
}
if (type == 1)
{
IntHandle(message);
}
else if (type == 2)
{
DoubleHandle(message);
}
else{
lg(Warning, "Type Error, type: %d ...", type);
}
}
}
}
void operator()()
{
run();
close(_socket_fd);
}
~Task()
{
}
private:
int _socket_fd;
};
4.serverCal.hpp
#pragma once
#include "Socket.hpp"
#include "protocol.hpp"
#include "threadPool.hpp"
#include "Task.hpp"
class ServerCal
{
public:
ServerCal()
{
}
void Init(const int sinfamily, const std::string &ip, const uint16_t port)
{
_listensock.Init();
_listensock.Bind(sinfamily, ip, port);
_listensock.Listen();
}
void Run()
{
daemon(0, 0); //仅此这里添加了一个守护线程功能
ThreadPool<Task> *tp = ThreadPool<Task>::GetInstance();
tp->Start();
struct sockaddr_in client;
while (true)
{
memset(&client, 0, sizeof client);
socklen_t len;
int socketfd = _listensock.Accept(&client, &len);
if (socketfd < 0)
continue;
tp->Push(socketfd);
}
}
private:
Socket _listensock;
};
这里我添加了守护线程的功能,使用的是系统库自带的函数。
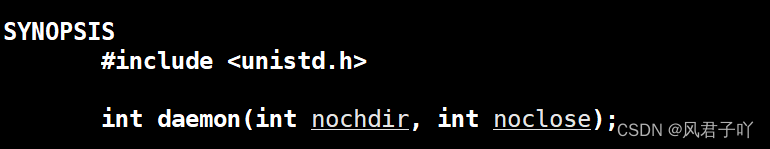
nochdir如果被设为0,则更改工作路径为“/”根目录,否则则什么也不敢。
noclose如果被设为0,则将标准输入输出错误重定向到/dev/null文件中,/dev/null文件我们上章是讲过的。
其他的文件我没有变动,需要的可以在我上一个文章复制粘贴或者到我的gitee自行拷贝。
新客户端
#include "Socket.hpp"
#include "protocol.hpp"
#define VALID_OP 5
const char valid_operator[VALID_OP] = {'+', '-', '*', '/', '%'};
static int localfd = -1;
void Usage(const char *mes)
{
std::cout << "Usage: " << mes << " ip[xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx] port[8080-9000]" << std::endl;
}
bool __CheckNumber(const std::string &str)
{
for (const char c : str)
{
if ((!isdigit(c)) && (c != '.'))
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
bool __CheckOp(const std::string &op)
{
if (op.size() != 1)
{
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < VALID_OP; i++)
{
if (op.find(valid_operator[i]) != std::string::npos)
break;
if (i == 4)
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
bool CheckSafe(const std::string &x, const std::string &op, const std::string &y, int *type)
{
if (!__CheckOp(op))
{
std::cout << "Helper: 使用了除 + - * / % 以外的运算符" << std::endl;
return false;
}
if (!__CheckNumber(x) || !__CheckNumber(y))
{
std::cout << "Helper: 请输入正确的数字" << std::endl;
return false;
}
if ((x.find('.') != std::string::npos) || (y.find('.') != std::string::npos))
{
// 说明这是浮点数运算
*type = 2;
return true;
}
*type = 1;
return true;
}
void IntHandle(const std::string &x, const std::string &op, const std::string &y, std::string &message)
{
IntRequest rq;
IntRespond rs;
rq._x = std::stoi(x);
rq._y = std::stoi(y);
rq._op = op[0];
rq.serialize(&message);
write(localfd, message.c_str(), message.size());
// 开始等待结果
char buffer[1024];
int n = read(localfd, buffer, sizeof buffer - 1);
if (n == 0)
{
lg(Warning, "Connection closed by foreign host, socketfd[%d] closed...", localfd);
exit(1);
}
else if (n < 0)
{
lg(Warning, "Read Error, socketfd[%d]...", localfd);
exit(2);
}
buffer[n] = 0;
std::string res = buffer;
std::cout << res << std::endl;
rs.deserialize(res);
if (rs._code != 0)
{
switch (rs._code)
{
case 1:
std::cout << "出现除0错误" << std::endl;
break;
case 2:
std::cout << "出现模0错误" << std::endl;
break;
case 3:
std::cout << "使用了除 + - * / % 以外的运算符" << std::endl;
break;
default:
std::cout << "发生未知错误" << std::endl;
break;
}
return;
}
printf("%d %c %d = %d
", rq._x, rq._op, rq._y, rs._result);
}
void DoubleHandle(const std::string &x, const std::string &op, const std::string &y, std::string &message)
{
DoubleRequest rq;
DoubleRespond rs;
rq._x = std::stod(x);
rq._y = std::stod(y);
rq._op = op[0];
rq.serialize(&message);
write(localfd, message.c_str(), message.size());
// 开始等待结果
char buffer[1024];
int n = read(localfd, buffer, sizeof buffer - 1);
if (n == 0)
{
lg(Warning, "Connection closed by foreign host, socketfd[%d] closed...", localfd);
exit(1);
}
else if (n < 0)
{
lg(Warning, "Read Error, socketfd[%d]...", localfd);
exit(2);
}
buffer[n] = 0;
std::string res = buffer;
std::cout << res << std::endl;
rs.deserialize(res);
if (rs._code != 0)
{
switch (rs._code)
{
case 1:
std::cout << "出现除0错误" << std::endl;
break;
case 2:
std::cout << "出现模0错误" << std::endl;
break;
case 3:
std::cout << "使用了除 + - * / % 以外的运算符" << std::endl;
break;
default:
std::cout << "发生未知错误" << std::endl;
break;
}
return;
}
printf("%lf %c %lf = %lf
", rq._x, rq._op, rq._y, rs._result);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != 3)
{
Usage("./clientCal");
}
Socket local;
local.Init();
int n = local.Connect(argv[1], argv[2]);
if (n < 0)
{
return 1;
}
localfd = local.Getfd();
std::cout << " 简易计算器, 目前仅支持\" + - * / %\"运算符 " << std::endl;
std::cout << " 数字和运算符请用空格或回车隔开" << std::endl;
std::string x, op, y;
int type;
std::string message;
while (true)
{
std::cout << "请输入您的算式@ ";
std::cin >> x >> op >> y;
if (!CheckSafe(x, op, y, &type))
{
continue;
}
std::cout << type << std::endl;
if (type == 1)
{
IntHandle(x,op,y,message);
}
else if(type ==2)
{
DoubleHandle(x,op,y,message);
}
else{
lg(Warning, "Type Error, type: %d ...", type);
exit(3);
}
}
return 0;
}
添加了许多输入的安全检查,不检查引发的问题太多了!



